Power internal tools, in-app experiences, and more
Overview
The MongoDB destination combines the analytical power of your data warehouse with the low-latency performance of a transactional database. It's been battle-tested with syncs up to hundreds of millions of rows.
Supported syncing
| Sync Type | Description | Supported Sync Modes |
|---|---|---|
| Documents | Sync data to documents in a MongoDB collection | Upsert |
Connect to MongoDB
Make sure to allowlist Hightouch IP addresses so Hightouch can reach your cluster. Refer to our IP address docs to find the relevant IP addresses for your Hightouch region. If you are using Atlas, you can add allowlist IP addresses from Security > Network Access.
When creating a MongoDB destination, you can either enter the Host, Port, Database, User, and Password, or you can provide the full URI connection string. For more information, go to the official connection guide.
SSH tunneling
Hightouch can connect directly to MongoDB over the public internet or via an SSH tunnel. Since data is encrypted in transit via TLS, a direct connection is suitable for most use cases. You may need to set up a tunnel if your MongoDB instance is on a private network or virtual private cloud (VPC).
Hightouch supports both standard and reverse SSH tunnels. To learn more about SSH tunneling, refer to Hightouch's tunneling documentation.
Retrieve MongoDB credentials
Assign the user whose credentials you use the built-in readWriteAnyDatabase MongoDB role or create a custom role and assign these actions at minimum:
| Action | Details |
|---|---|
insert | Grants permission to perform insert and create commands |
remove | Grants permission to perform the delete command |
update | Grants permission to perform the update command |
listIndexes | Grants permission to perform the listIndexes command |
listCollections | Grants permission to perform the listCollections command |
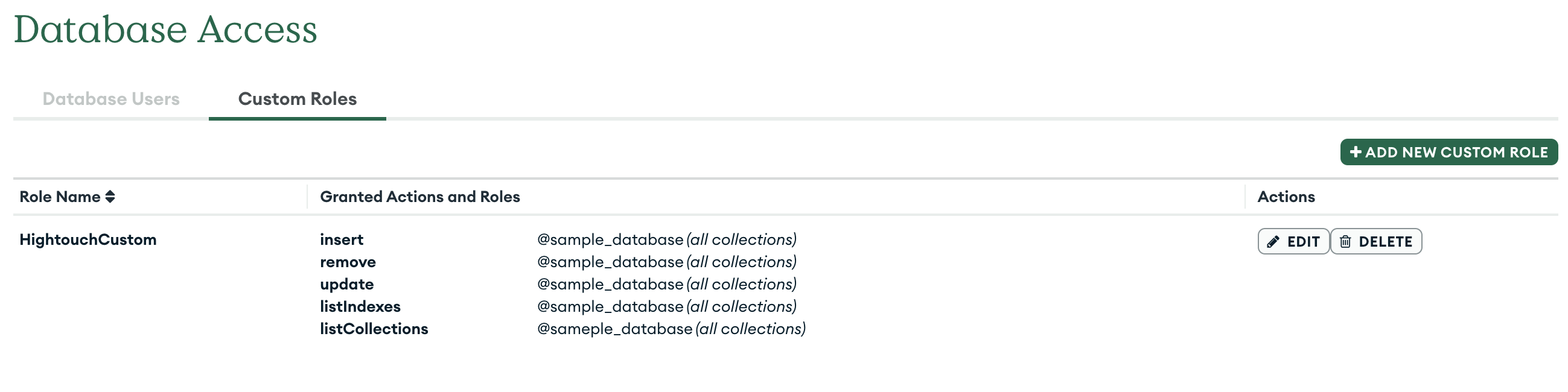
To create a user in MongoDB, use db.createUser().
Authenticate with connection parameters
Enter the following required fields into Hightouch:
- Host: The hostname or IP address of your MongoDB server. For help finding this, go to the official connection guide.
- Port: The port number of your MongoDB server. The default port number is 27017, but yours may be different. You don't need to specify the port if you are using SRV protocol.
- Database: The name of the your MongoDB database.
- Username: This can be your personal MongoDB login or a dedicated user for Hightouch.
- Password: This is the password for the user specified above. If you're using Atlas, the user password might differ from the one you use to login to your MongoDB Atlas instance.
- Is the host name a seedlist record?: To use SRV protocol (Hightouch defaults to standard), you must toggle this setting. If you are using MongoDB Atlas and the connection string begins with protocol
mongodb+srv, toggle this setting to connect.
Authenticate with connection string
The connection string is available in multiple locations. Follow these instructions for one way to find it.
-
From the MongoDB UI click the Connect button next to the name of your cluster:
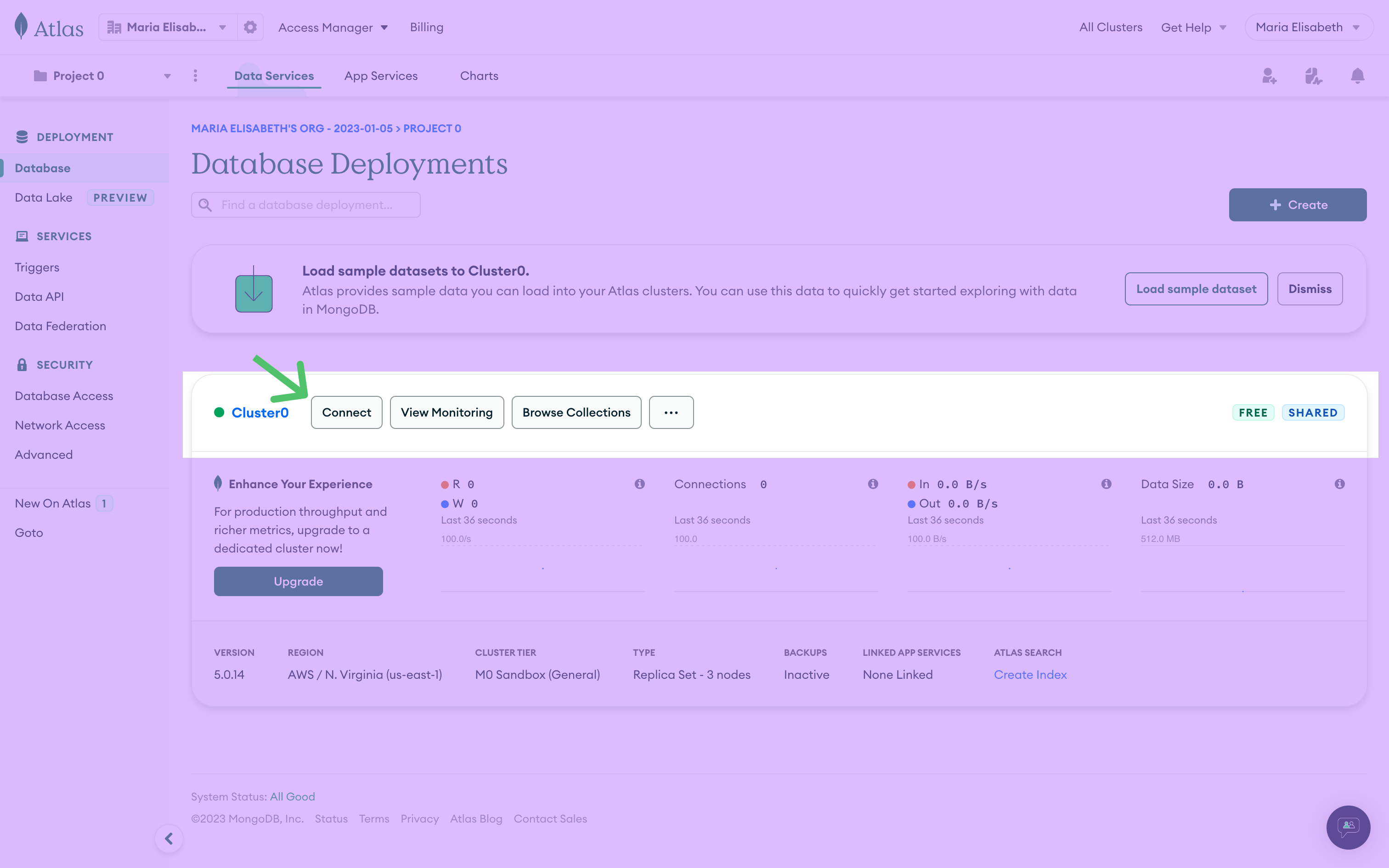
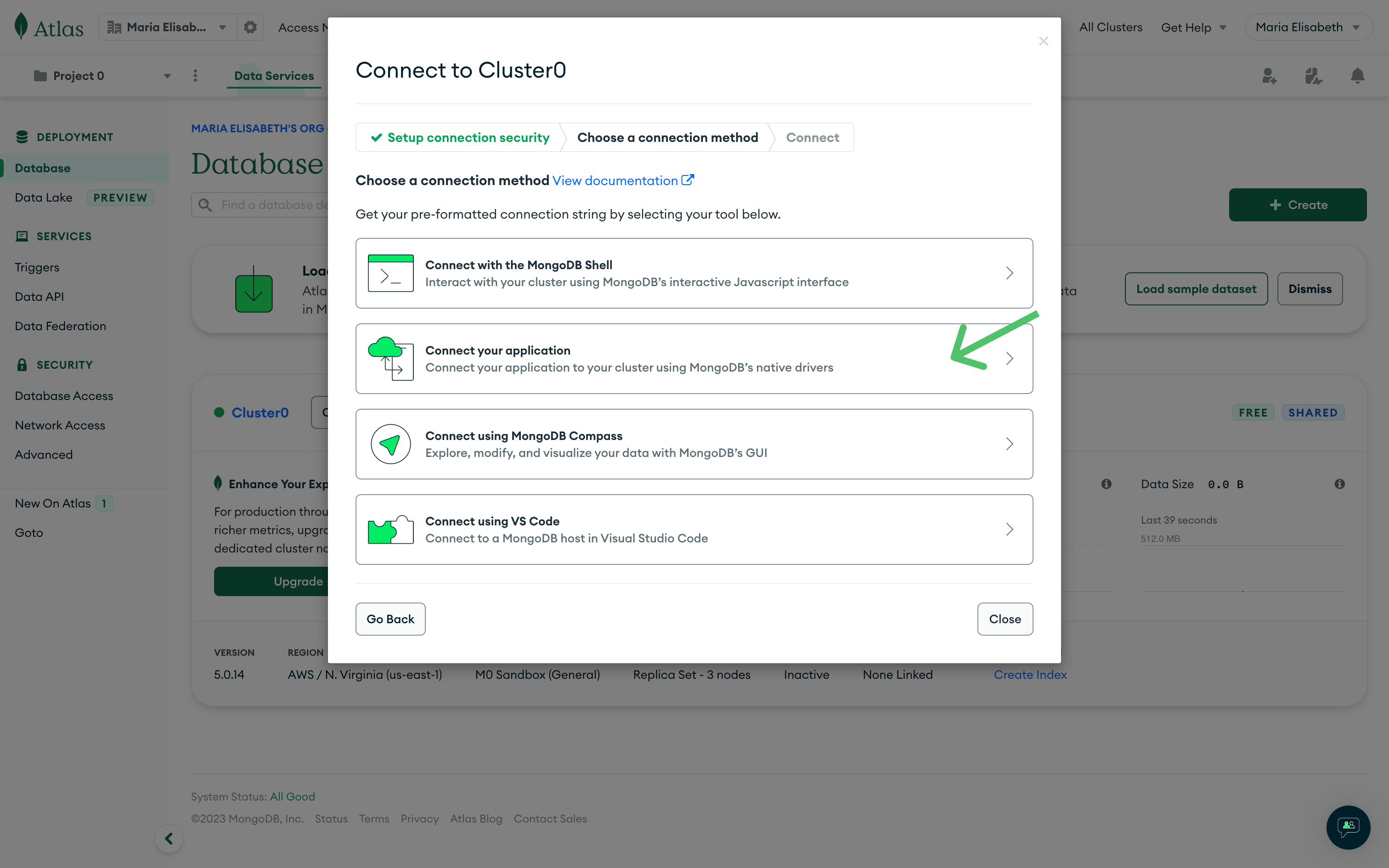
-
From the options displayed, select Connect your application:
Follow the instructions for changing the password and database name in the string. Copy the string by clicking the copy icon:
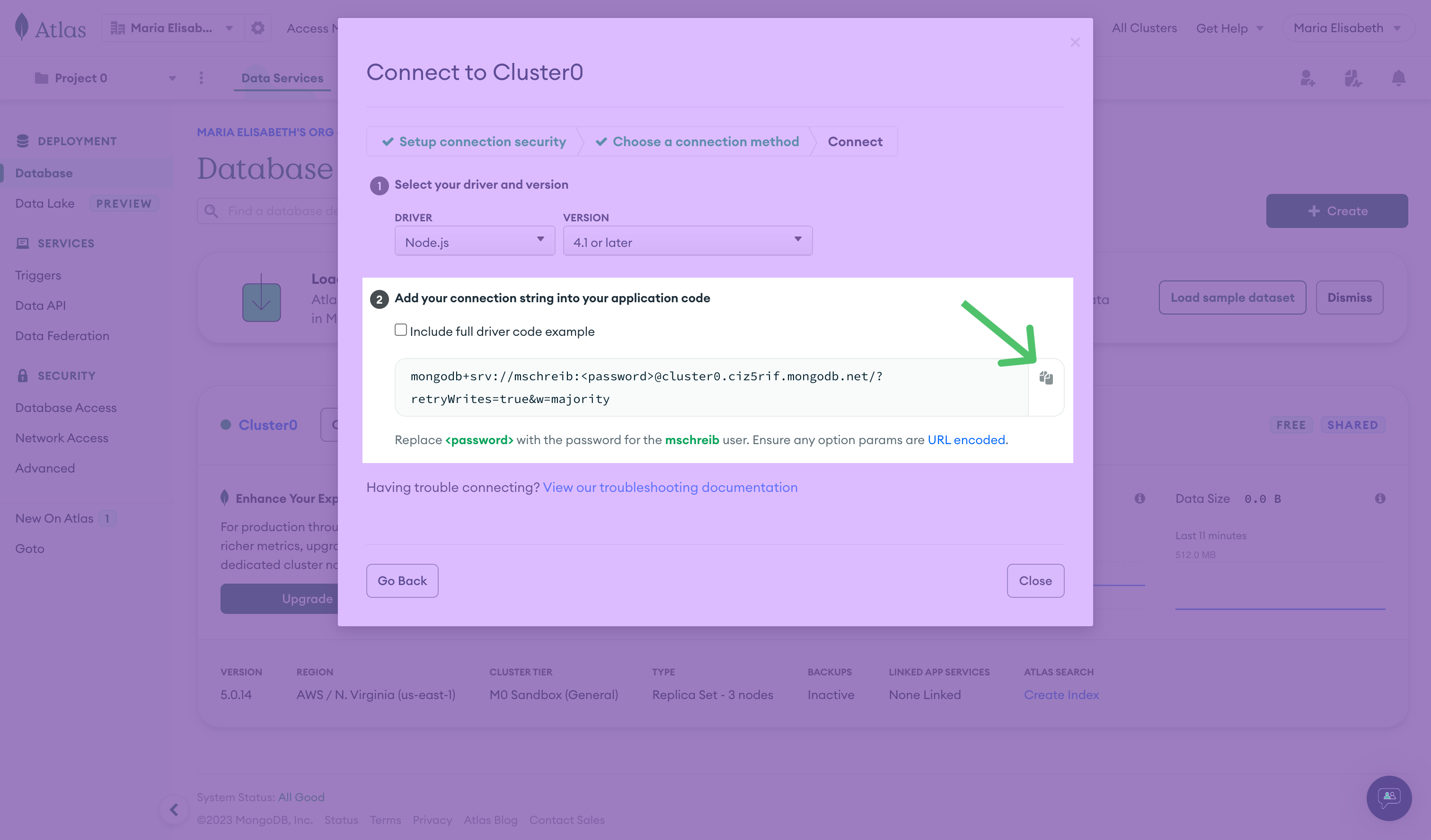
In Hightouch, in the MongoDB setup configuration, paste your saved connection string into the provided field.
Sync configuration
Record matching
Hightouch requires choosing one column to define how to match data in your source to documents in MongoDB. It's usually best to use the _id field in MongoDB. Otherwise, you can also select _id (Object ID) if you already have Object ID values in your source data.
You can also choose to record match on a custom MongoDB field. To do this, you need to create a unique index on a single field, which is a specific type of single field index. Before creating this index, make sure that the field doesn't contain duplicate values, as this makes the index build fail with an Unknown error message.
If you record match on a custom field, MongoDB automatically generates an Object ID to insert in the _id field.
Field mapping
You can map the columns you want to include when creating new MongoDB documents or updating existing ones by selecting the model column and typing the respective MongoDB field name. Otherwise, you can include every column from your model by checking the Sync all columns box.
Delete behavior
You can choose how to handle documents in MongoDB when the corresponding rows are deleted in your source.
| Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Do nothing | Keep the document in MongoDB |
| Clear Fields | Clear the mapped fields but keep the document |
| Delete Destination Record | Delete the MongoDB document completely |
Tips and troubleshooting
Best practices
Create a user in MongoDB specifically for Hightouch and only allow that user to access the collections you want Hightouch to access. Don't use the 'root' user.
Compatible versions
The minimum supported MongoDB version is 4.0. Earlier versions aren't officially supported but may work regardless.
Common errors
MongoServerError: bad auth: Authentication failed
This error can occur if the destination wasn't configured correctly. Make sure to use the correct password for the user specified in the configuration. If the error is still happening, try changing your MongoDB user's password and attempting the setup again.
Live debugger
Hightouch provides complete visibility into the API calls made during each of your sync runs. We recommend reading our article on debugging tips and tricks to learn more.
Sync alerts
Hightouch can alert you of sync issues via Slack, PagerDuty, SMS, or email. For details, please visit our article on alerting.
